Choosing the Right Safety Glass for Shopfronts and Retail Spaces
Glass façades in retail environments must balance beauty, security, and safety compliance. The right choice of safety glass can protect customers, reduce liability, and preserve aesthetics. Here’s how to make the right decision.
Why Safety Glass Matters in Retail
Shopfronts, display windows, and glass doors are exposed to both public traffic and environmental stress. Using non-safety glass can result in serious injuries, insurance issues, and costly downtime. Safety glass prevents shattering, resists impact, and keeps the premises secure even after breakage.
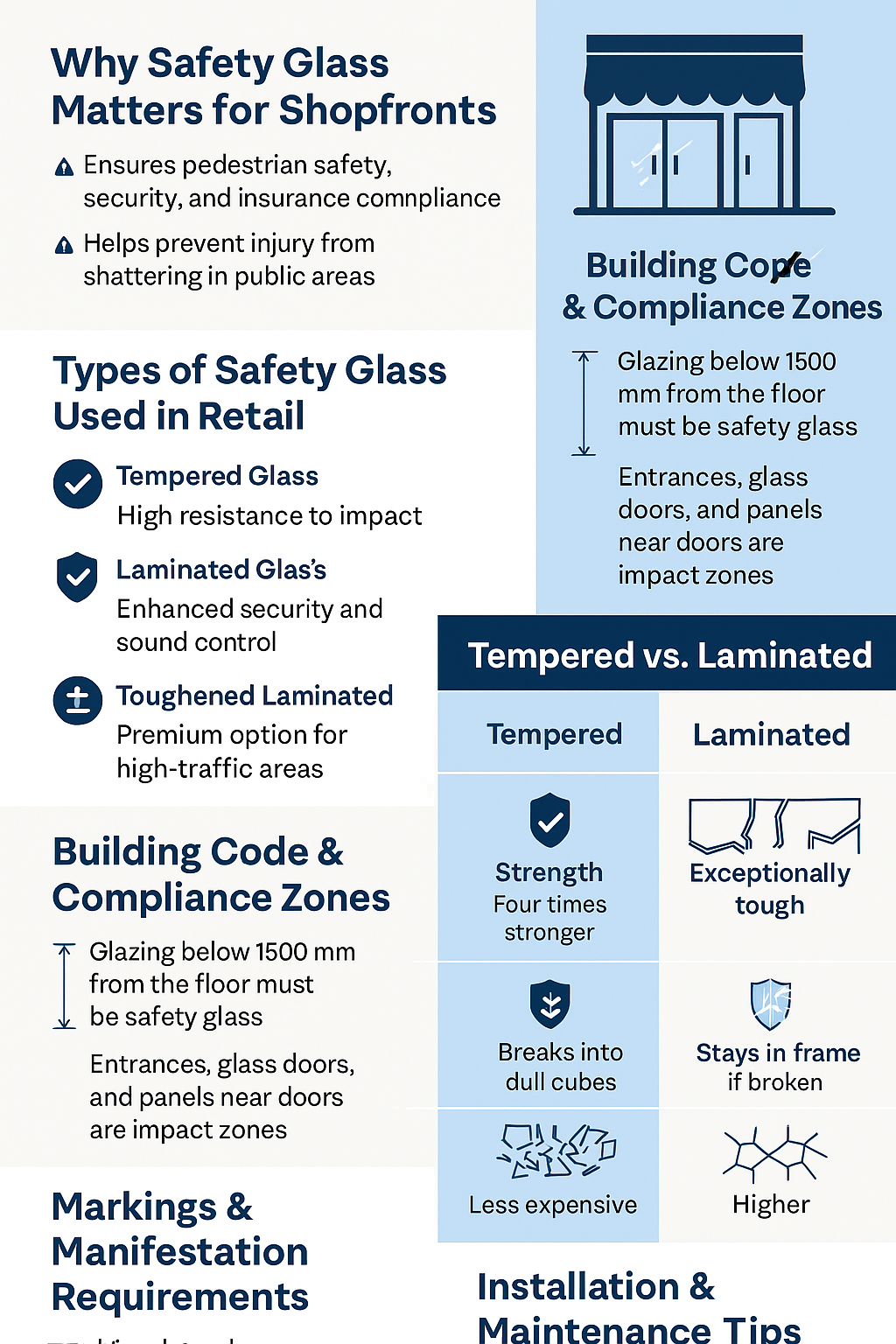
Types of Safety Glass for Retail Use
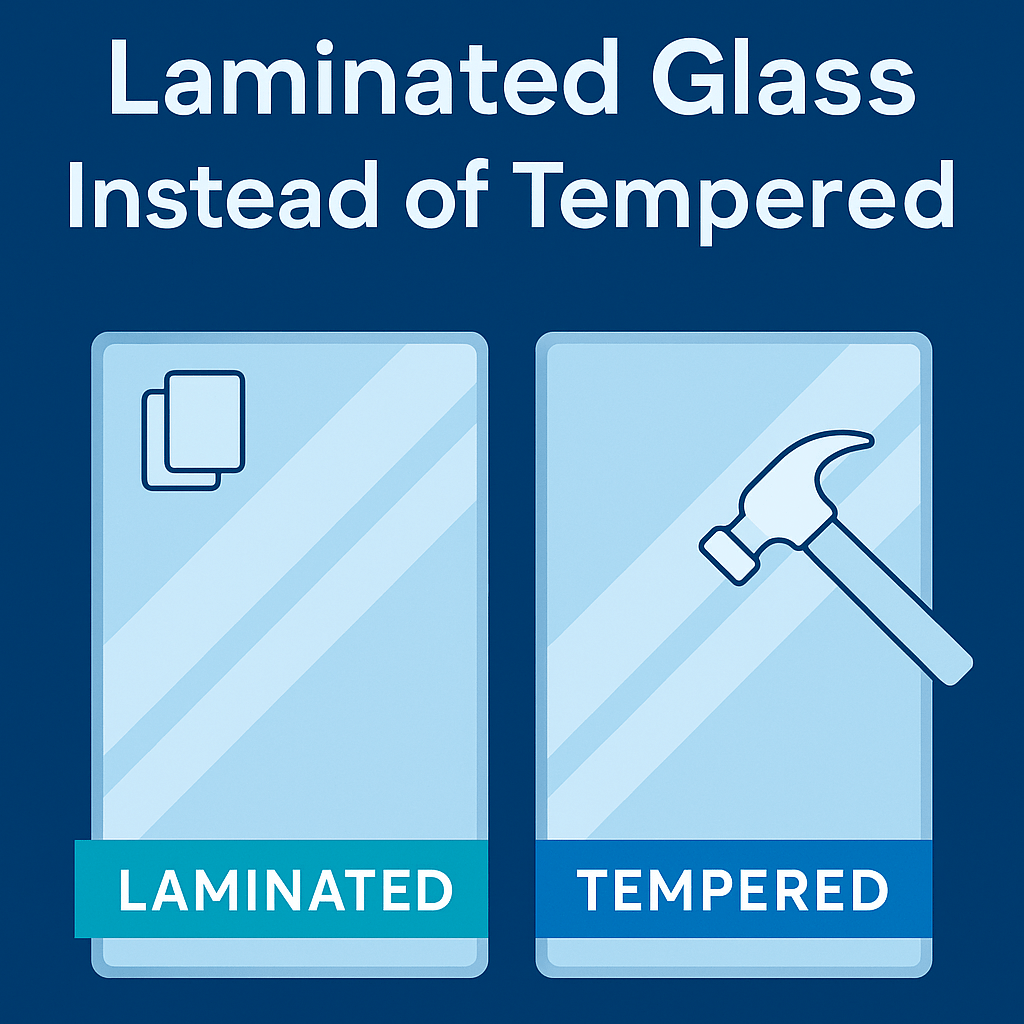
- Tempered Glass: Heat-treated for impact resistance; breaks into small blunt fragments.
- Laminated Glass: Two or more panes bonded with a durable interlayer that holds fragments in place.
- Toughened Laminated: Combines the strength of tempering with the containment of lamination — ideal for busy shopfronts.
Code Requirements & Impact Zones
Safety glazing is required by code in all “hazardous locations,” including doors, sidelights, low glazing below 1500 mm, and windows adjacent to walkways. Always check ANSI Z97.1 and CPSC 16 CFR 1201 for applicable categories and test standards.
Tempered vs. Laminated: Side-by-Side Comparison
Markings & Visibility Requirements
For public safety, glass in shopfronts and entrances must include visible manifestation such as frosting, decals, or etched logos at eye level. Glass should also carry an etched compliance mark verifying that it meets ANSI or CPSC safety glazing standards.
Installation & Maintenance Tips
- Hire certified installers familiar with safety glazing codes.
- Check for ANSI/CPSC etch marks before installation.
- Inspect for cracks or edge damage regularly, especially on high-traffic doors.
- Clean with non-abrasive materials to preserve the safety film and seals.
Further Reading
For those interested in understanding how tempered and laminated glass differ in structural and safety performance, see
this detailed guide on GlassHelp — a practical reference explaining impact classifications and architectural glazing standards.





Leave a comment