When to Choose Laminated Glass Instead of Tempered
Laminated glass is often overlooked in favor of tempered glass — but in many applications, it’s the smarter, safer choice. This article helps you understand its advantages, test its use cases, and decide when it’s best for your projects.
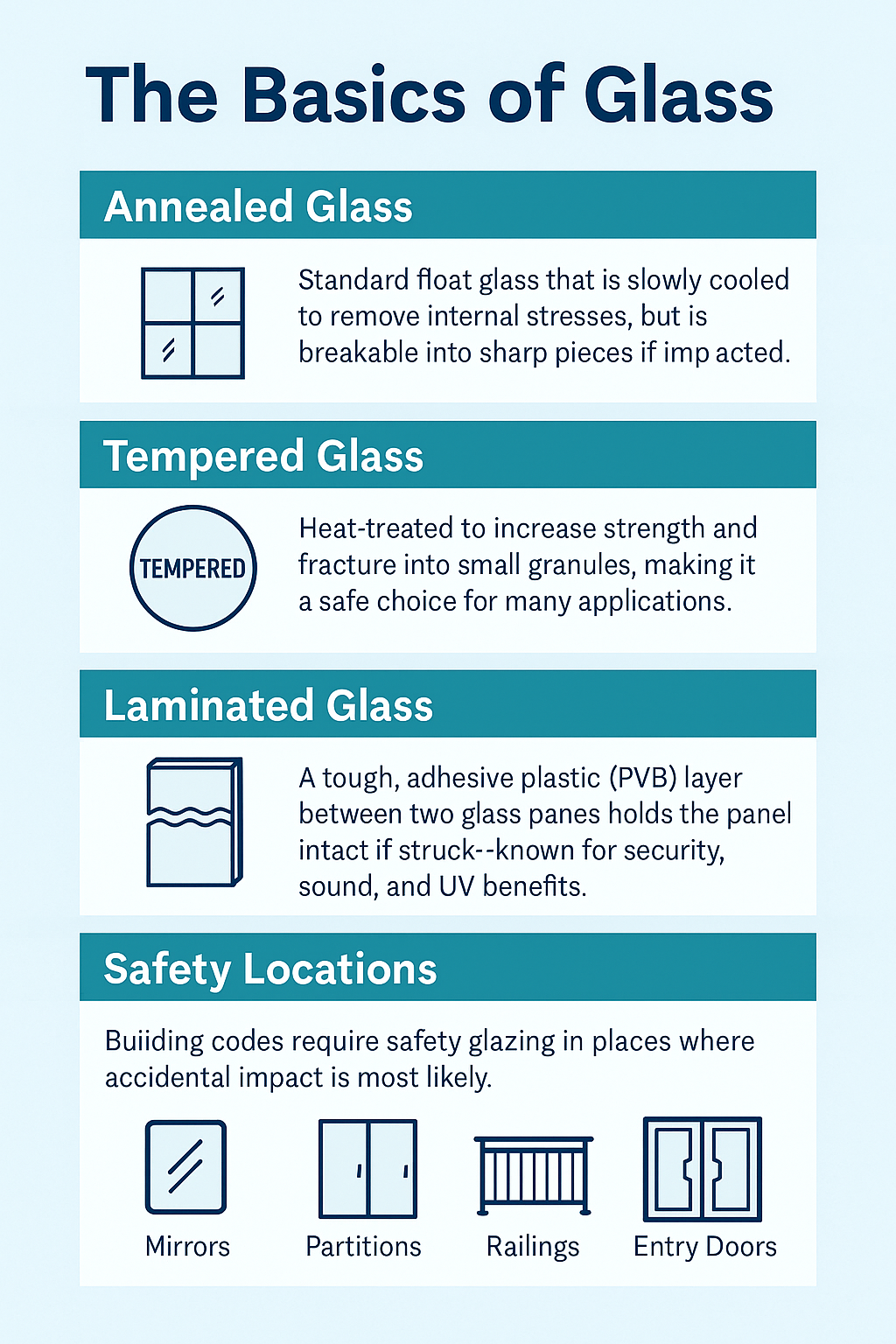
What Is Laminated Glass?
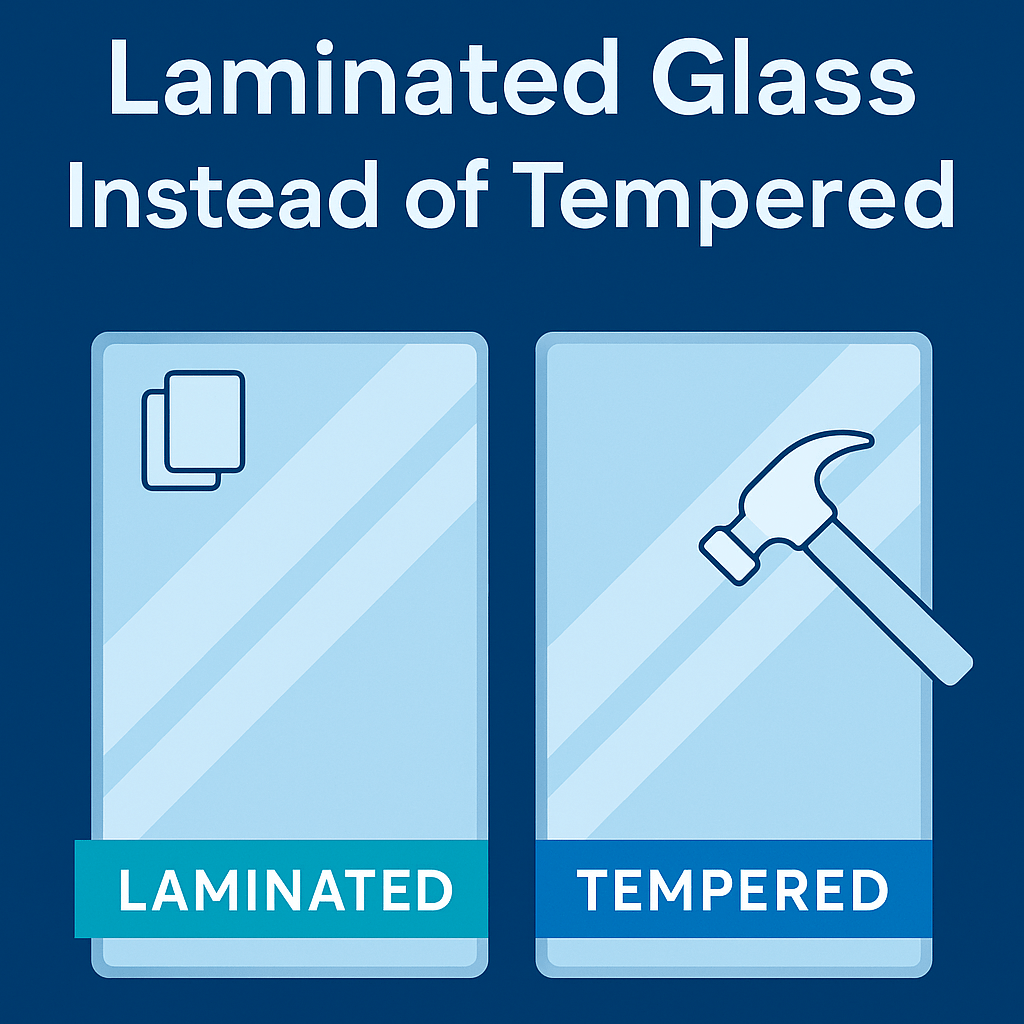
Laminated glass consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together by an interlayer — typically PVB, EVA, or SentryGlas®. When impacted, the glass may crack but stays adhered to the interlayer, preventing dangerous shards from falling.
This unique structure makes laminated glass ideal for situations where containment, sound insulation, or UV protection is required — providing safety beyond what tempered glass alone can achieve.
How Laminated Differs from Tempered
- Breakage: Tempered shatters into small fragments; laminated holds together even when cracked.
- Impact Resistance: Tempered glass absorbs high stress before breaking; laminated glass maintains integrity after breakage.
- Safety: Laminated glass prevents fall-through hazards and keeps openings sealed post-breakage.
- Applications: Laminated excels where human impact or containment is critical — overhead glazing, balustrades, and facades.
Key Benefits of Laminated Glass
1. Post-break Safety
Holds together after impact, reducing injury and fall-through risks.
2. Acoustic Control
Interlayer absorbs sound waves, improving comfort in offices and homes.
3. UV & Fade Protection
Blocks over 99% of UV rays, preventing interior fading.
4. Security & Burglary Resistance
Harder to penetrate — ideal for storefronts and display glazing.
5. Customizable
Available in tinted, frosted, or decorative interlayers.
6. Compliance Ready
Meets OSHA, ANSI Z97.1, and CPSC 16 CFR 1201 when properly rated.
Best Applications for Laminated Glass
- Overhead glazing, skylights, and canopies
- Balustrades, railings, and stair barriers
- Soundproof office partitions and meeting rooms
- Storefronts and display windows with anti-burglary protection
- Museum cases and protective enclosures
- Buildings in high-wind or hurricane zones
Compliance & Safety Standards
Laminated glass is recognized under major U.S. safety glazing standards — ANSI Z97.1 and CPSC 16 CFR 1201 — provided it passes the same impact and penetration tests as tempered glass.
OSHA also references these standards to ensure workplace safety.
Always confirm your laminated glass product carries the correct etched certification mark and has been tested for its intended use.
Laminated vs Tempered Glass: Quick Comparison
Learn More About Safety Glass
To explore safety glazing in more depth and compare laminated vs. tempered solutions for UK projects, visit
GlassHelp — Tempered Glass.
This guide provides further insights into building compliance and the correct applications for safety glass in both residential and commercial environments.





Leave a comment